Shoulder Replacement Surgery:
A Comprehensive Guide to
Restoring Function and Easing Pain
Ever dealt with that persistent shoulder ache that just won’t go away?
Life can throw some unexpected twists, and sometimes our shoulders bear the brunt – blame it on overdoing activities or just plain bad luck.
Now, picture this: your shoulder suddenly decides to act up.
It’s not just a minor annoyance; it’s a constant bother.
So, what if the usual fixes – rest, therapy, and meds
– don’t quite do the trick? What do to do then?
Watch out for the shoulder situation. If it’s making your day a bit too painful, especially when you’re just trying to do simple things, like reaching for something, it might be time to seek professional advice to understand your shoulder’s needs.
Your well-being is essential, and finding the right solution will help bring comfort back to your shoulder. Here’s an overview of a surgery that might be the answer to your shoulder pain – Shoulder replacement surgery
Understanding Shoulder Replacement Surgery
The shoulder, a complex and highly mobile joint, is susceptible to various issues such as wear and tear, arthritis, and traumatic injuries. When conservative treatments prove inadequate, Shoulder Replacement Surgery emerges as a comprehensive solution.
Shoulder replacement is a surgical intervention that entails the replacement of damaged or diseased parts of the shoulder joint with meticulously crafted artificial components. The primary objective is two-fold:
> To alleviate debilitating pain and,
> To restore a full range of motion, thereby enhancing
the overall quality of life for the patient.
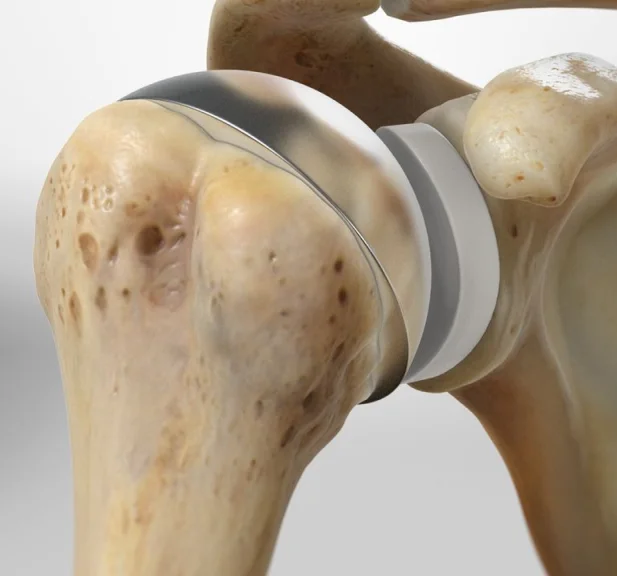
Indications for Shoulder Replacement Surgery
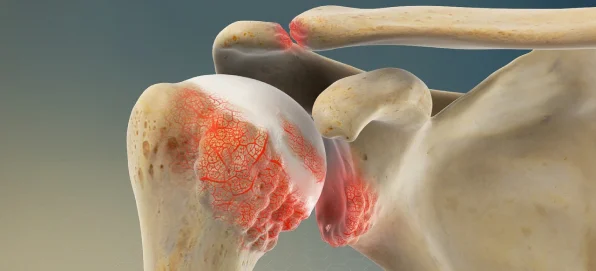
Osteoarthritis
A degenerative condition leading
to the deterioration of joint cartilage.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
An autoimmune-related inflammation
affecting the joints.
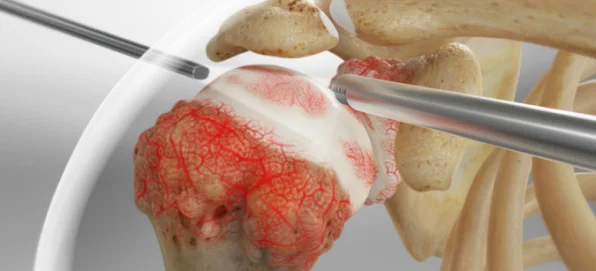
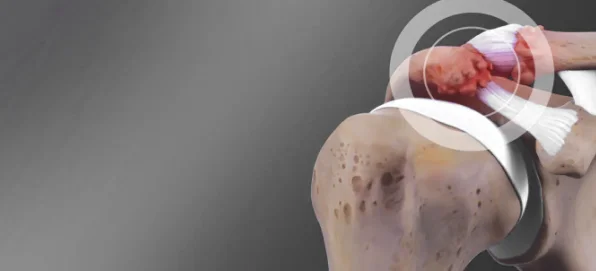
Post-Traumatic Arthritis:
Arising from severe shoulder injuries.
Rotator Cuff Tears:
Tears that impact joint function.
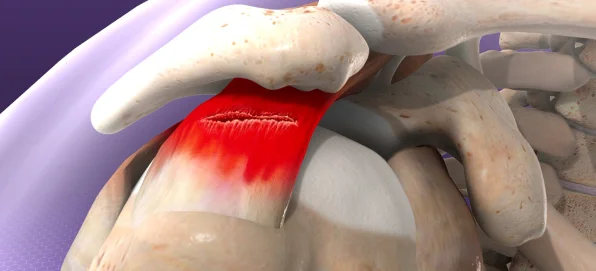
Avascular Necrosis:
A condition characterized by poor
blood supply leading to bone death
Types of Shoulder Replacement: A Tailored Approach
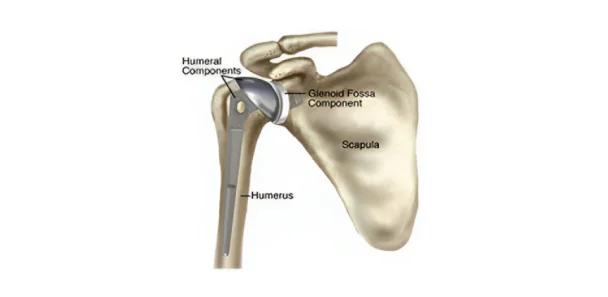
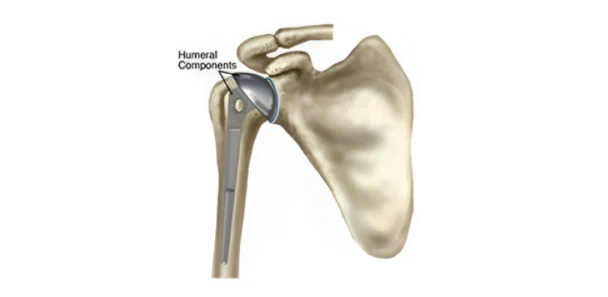
Total Shoulder Replacement (TSR):
> In this procedure, both the ball and socket of the shoulder joint are replaced with prosthetic components.
>TSR is often recommended for cases of severe arthritis or extensive joint damage.
Partial Shoulder Replacement
(Hemiarthroplasty):
>Hemiarthroplasty involves replacing only the ball of
the shoulder joint, preserving the natural socket.
>It is a suitable option for specific fractures or
limited arthritis.
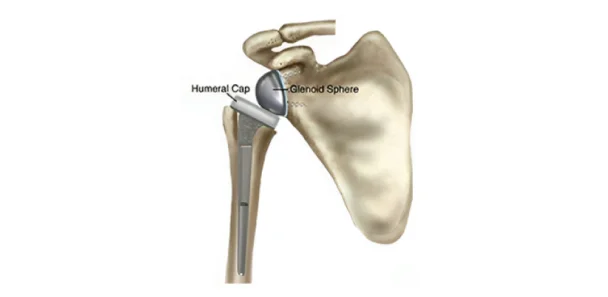
Reverse Shoulder Replacement:
>Specifically designed for patients with irreparable rotator cuff tears.
>This innovative approach reverses the ball-and-socket configuration, placing the ball in the shoulder socket and the socket on the upper arm.
The Surgery Process
Recovery